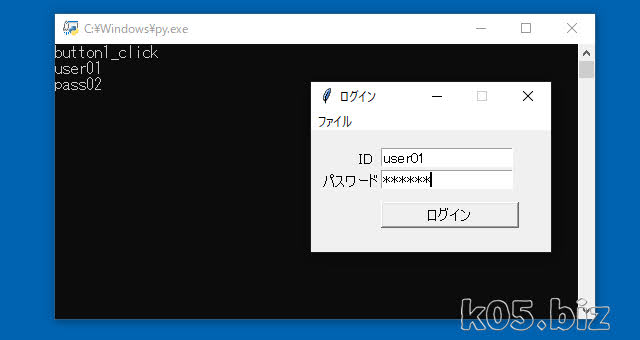
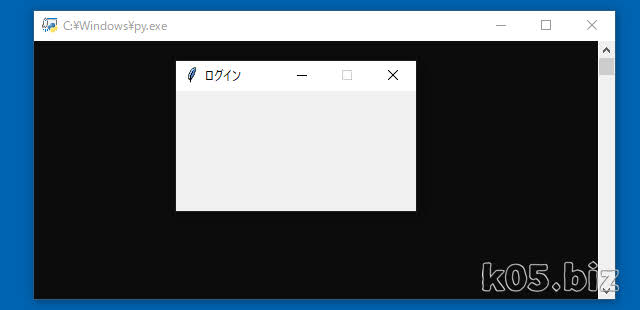
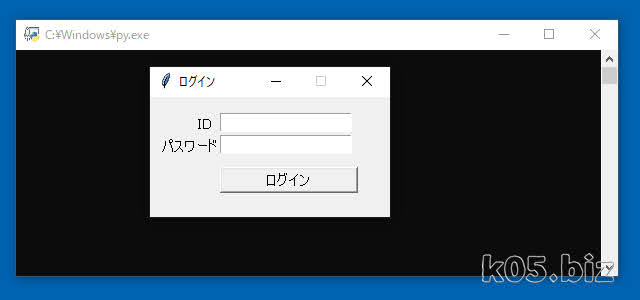
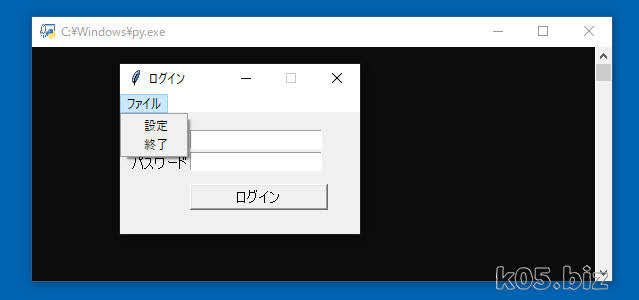
こんな感じのフォームをPythonで作成してみます。Tkinterを使いますが、標準で入っているライブラリーです。
Windows表示まで
import tkinter as tk
#===========================
# メイン 関数
#===========================
def main():
#-----------------------
# Window作成
#-----------------------
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("ログイン")
root.geometry("240x120")
root.resizable(False, False)
#-----------------------
# イベント待機
#-----------------------
root.mainloop()
#===========================
# 実行
#===========================
main()
まずは、Windowの表示までです。「root.resizable(False, False)」で、Windowsのサイズを変更できないようにしています。
画面レイアウト表示まで
import tkinter as tk
#===========================
# メイン 関数
#===========================
def main():
#-----------------------
# Window作成
#-----------------------
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("ログイン")
root.geometry("240x120")
root.resizable(False, False)
#-----------------------
# フォント指定
#-----------------------
root.option_add('*Label.font', ["MS UI Gothic",11])
root.option_add('*Entry.font', ["MS UI Gothic",11])
root.option_add('*Button.font', ["MS UI Gothic",11])
#-----------------------
# ラベル
#-----------------------
label1 = tk.Label(root)
label1["text"] = "ID"
label1.place(x=45,y=16)
label2 = tk.Label(root)
label2["text"] = "パスワード"
label2.place(x=9,y=38)
#-----------------------
# テキストボックス
#-----------------------
textbox1 = tk.Entry(root)
textbox1["width"] = 16
textbox1.place(x=70,y=16)
textbox2 = tk.Entry(root)
textbox2["width"] = 16
textbox2["show"] = '*'
textbox2.place(x=70,y=38)
#-----------------------
# ボタン
#-----------------------
button1 = tk.Button(root)
button1["text"] = "ログイン"
button1["width"] = 16
button1.place(x=70,y=70)
#-----------------------
# イベント待機
#-----------------------
root.mainloop()
#===========================
# 実行
#===========================
main()
ウィジェットの配置には、「pack、grid、place」がありますが、座標指定で配置したい場合は、placeを使います。
label1.place(x=45,y=16)のように、座標指定で配置できるので、VB(VBA)ライクに配置できます。
ボタンのクリックイベントの処理を書く
import tkinter as tk
#===========================
# ボタン clickイベント関数
#===========================
def button1_click():
print("button1_click")
print(textbox1.get())
print(textbox2.get())
#===========================
# メイン 関数
#===========================
def main():
global root
global textbox1
global textbox2
#-----------------------
# Window作成
#-----------------------
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("ログイン")
root.geometry("240x120")
root.resizable(False, False)
#-----------------------
# フォント指定
#-----------------------
root.option_add('*Label.font', ["MS UI Gothic",11])
root.option_add('*Entry.font', ["MS UI Gothic",11])
root.option_add('*Button.font', ["MS UI Gothic",11])
#-----------------------
# ラベル
#-----------------------
label1 = tk.Label(root)
label1["text"] = "ID"
label1.place(x=45,y=16)
label2 = tk.Label(root)
label2["text"] = "パスワード"
label2.place(x=9,y=38)
#-----------------------
# テキストボックス
#-----------------------
textbox1 = tk.Entry(root)
textbox1["width"] = 16
textbox1.place(x=70,y=16)
textbox2 = tk.Entry(root)
textbox2["width"] = 16
textbox2["show"] = '*'
textbox2.place(x=70,y=38)
#-----------------------
# ボタン
#-----------------------
button1 = tk.Button(root)
button1["text"] = "ログイン"
button1["width"] = 16
button1["command"] = button1_click
button1.place(x=70,y=70)
#-----------------------
# イベント待機
#-----------------------
root.mainloop()
#===========================
# 実行
#===========================
main()
button1["command"] = button1_click で、ボタンのクリック時に処理する関数を指定します。で、def button1_click():で、実際に処理したい内容を記述します。
あと、外部から参照するために、「global root、global textbox1、global textbox2」のように、global 指定しています。たぶん、あまりよくない実装なのかもと思う。クラス化すれば解消はできるとは思う。
メニューバーを追加する
import tkinter as tk
#===========================
# ボタン clickイベント関数
#===========================
def button1_click():
print("button1_click")
print(textbox1.get())
print(textbox2.get())
#===========================
# メニュー clickイベント関数
#===========================
def menu_end_click():
print("menu_end_click")
root.destroy()
#===========================
# メイン 関数
#===========================
def main():
global root
global textbox1
global textbox2
#-----------------------
# Window作成
#-----------------------
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("ログイン")
root.geometry("240x120")
root.resizable(False, False)
#-----------------------
# フォント指定
#-----------------------
root.option_add('*Label.font', ["MS UI Gothic",11])
root.option_add('*Entry.font', ["MS UI Gothic",11])
root.option_add('*Button.font', ["MS UI Gothic",11])
#-----------------------
# ラベル
#-----------------------
label1 = tk.Label(root)
label1["text"] = "ID"
label1.place(x=45,y=16)
label2 = tk.Label(root)
label2["text"] = "パスワード"
label2.place(x=9,y=38)
#-----------------------
# テキストボックス
#-----------------------
textbox1 = tk.Entry(root)
textbox1["width"] = 16
textbox1.place(x=70,y=16)
textbox2 = tk.Entry(root)
textbox2["width"] = 16
textbox2["show"] = '*'
textbox2.place(x=70,y=38)
#-----------------------
# ボタン
#-----------------------
button1 = tk.Button(root)
button1["text"] = "ログイン"
button1["width"] = 16
button1["command"] = button1_click
button1.place(x=70,y=70)
#-----------------------
# メニューバー
#-----------------------
menubar1 = tk.Menu(root)
root.config(menu=menubar1 )
menu_file = tk.Menu(menubar1, tearoff=0)
menubar1.add_cascade(label='ファイル', menu=menu_file)
menu_file.add_command(label='設定')
menu_file.add_command(label='終了', command = menu_end_click)
#-----------------------
# イベント待機
#-----------------------
root.mainloop()
#===========================
# 実行
#===========================
main()
クラス化
https://docs.python.org/3/library/tkinter.html
上記の「A Simple Hello World Program」というサンプルを参考にして、クラスを使った書き方に変更してみます。
ネットで見かける解説の多くは、上記のサンプルをベースに書いていると思います。
import tkinter as tk
#===========================
# Application クラス
#===========================
class Application(tk.Frame):
#-----------------------
# コンストラクタ
#-----------------------
def __init__(self, master=None):
super().__init__(master)
master.title("ログイン")
master.geometry("240x120")
master.resizable(False, False)
master.option_add('*Label.font', ["MS UI Gothic",11])
master.option_add('*Entry.font', ["MS UI Gothic",11])
master.option_add('*Button.font', ["MS UI Gothic",11])
self.create_widgets(master=master)
#-----------------------
# ウィジェット 生成
#-----------------------
def create_widgets(self,master):
self.label1 = tk.Label(master)
self.label1["text"] = "ID"
self.label1.place(x=45,y=16)
self.label2 = tk.Label(master)
self.label2["text"] = "パスワード"
self.label2.place(x=9,y=38)
self.textbox1 = tk.Entry(master)
self.textbox1["width"] = 16
self.textbox1.place(x=70,y=16)
self.textbox2 = tk.Entry(master)
self.textbox2["width"] = 16
self.textbox2["show"] = '*'
self.textbox2.place(x=70,y=38)
self.button1 = tk.Button(master)
self.button1["text"] = "ログイン"
self.button1["width"] = 16
self.button1["command"] = self.button1_click
self.button1.place(x=70,y=70)
self.menubar1 = tk.Menu(master)
master.config(menu=self.menubar1 )
self.menu_file = tk.Menu(self.menubar1, tearoff=0)
self.menubar1.add_cascade(label='ファイル', menu=self.menu_file)
self.menu_file.add_command(label='設定')
self.menu_file.add_command(label='終了', command = master.destroy)
#-----------------------
# ボタン clickイベント
#-----------------------
def button1_click(self):
print("button1_click")
print(self.textbox1.get())
print(self.textbox2.get())
#===========================
# メイン 関数
#===========================
def main():
root = tk.Tk()
app = Application(master=root)
app.mainloop()
#===========================
# 実行
#===========================
main()
ほとんど、書いてる内容は変わりませんけどね。クラス化が分からないのなら、スルーして、別に好きなように書けばよいと思います。
動画での説明
動画のように、少しずつコードを追加しながら、理解していくのがお勧めかも。
スポンサーリンク